Project structure¶
The following picture shows all of the components (modules) of the Maven project hosted at https://github.com/eclipse/steady. Each component visible in the picture corresponds to a module listed in the pom.xml. The component (module) dependencies shown are of three kinds: Dependencies with Maven scopes COMPILE or RUNTIME and REST calls happening at runtime.
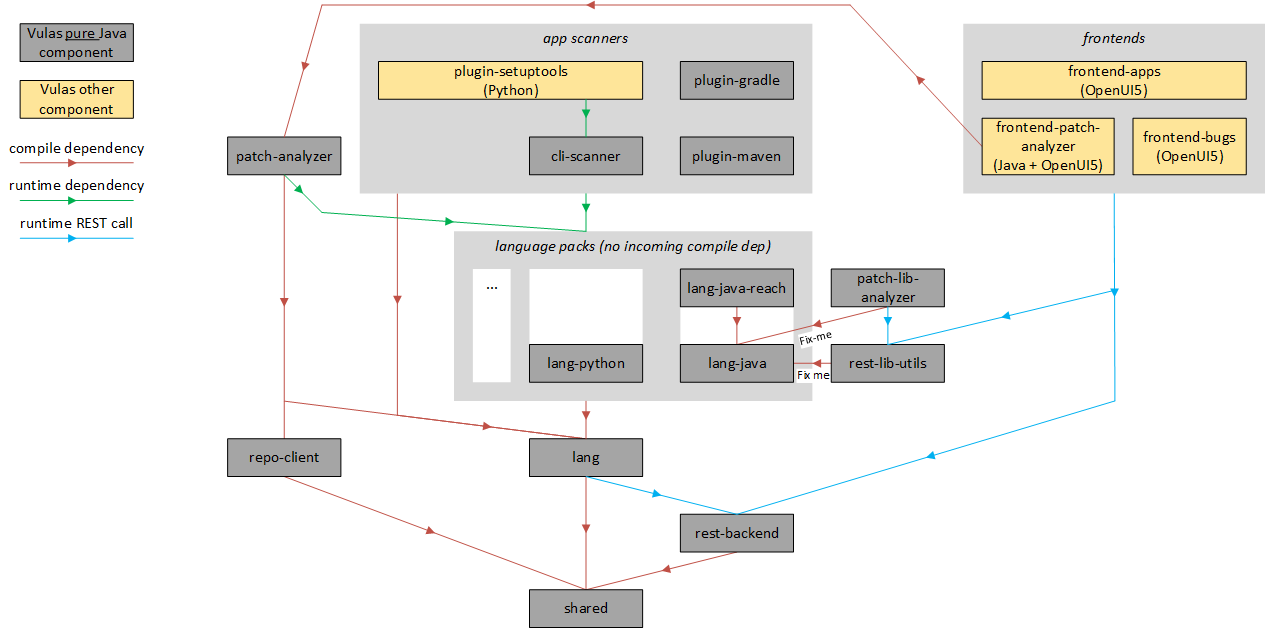
The project comprises the following client-side tools to scan Java and Python applications. All of those run on a client, typically a Jenkins build server or a developer work station.
plugin-mavenscans Java applications developed with Java and Maven (based on the application-specificpom.xml)plugin-gradlescans Java applications developed with Java and Gradle (based on the application-specificbuild.gradle)cli-scannerscans both Java and Python applications (based on code present in the file system)plugin-setuptoolsscans Python applications (based on the application-specificsetup.py). Important: This component is not yet part of the GitHub repo https://github.com/eclipse/steady.
Those client-side tools have just one COMPILE dependency on the language-agnostic component lang, which comprises a number of general functionality related to, for instance, backend connectivity or language-agnostic goals such as clean or report.
The client-side tools also have RUNTIME dependencies on language-specific components. The motivation to use RUNTIME dependencies is to keep the client-side tools free of language-specific code.
The project comprises the following frontends, all of them developed using OpenUI5:
frontend-appsis used by application developers to check scan results or their applicationfrontend-bugsis used by administrators to check and maintain bug informationfrontend-patch-analyzeris used by administrators to trigger the analysis of fix commits. Important: This component is outdated, the analysis of fix commits is done using thepatch-analyzercommand-line tool.
The language-specific component comprise all the logic to analyze source and compiled code as well as the various package formats of the respective programming language, e.g., JARs and WARs in case of Java. For Java, there also exist several modules related to the static analysis, namely lang-java-reach, lang-java-reach-wala and lang-java-reach-soot.
There exist the following two server-side components, both of them exposing a RESTful interface browsable through Swagger:
rest-backendis connected to a PostgreSQL database in order to store and join vulnerability information and application analysis resultsrest-lib-utilsanalyses Java archives in order to, for instance, obtain Abstract Syntax Trees for Java methods comprises in given Maven artifacts
The remaining components are as follows:
repo-clientsupports interactions with Git and SVN repositoriespatch-lib-analyzerdetermines whether open source components comprise the affected (vulnerable) or the fixed version of a given methodssharedcomprises utilities, model classes used for (de)serialization and other general functionality relevant for all other componentspatch-analyzerexamines the fix commit(s) of a given vulnerability in order to understand which methods have been changed in order to fix the vulnerability