Namespaces | |
| BoundingVolumes | |
| CsvReader | |
| funop | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef interval< double > | idouble |
| typedef interval< float > | ifloat |
| typedef interval< int > | iint |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 1 > | velocity_profile |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 3 > | function_type_xyz |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 2 > | function_type2d |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 1 > | function_type_scalar |
Functions | |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, N > * | sample_adaptive (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *f, ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *df, T edes, T emax, T xmin, T xmax, T xstep, T precision=(T) 0.0001) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | set (T *data, T value, int size) |
| template<typename T > | |
| adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > | sequence (T x0, T dx, T xend) |
| template<typename T > | |
| int | sequence (T x0, T dx, T xend, T *target, int max_size) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | sequence (T x0, T dx, T *target, int size) |
| template<typename T , int n> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, 1, n > | linspace (T x0, T x1) |
| template<typename T > | |
| adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > | linspace (T x0, T x1, int n) |
| template<typename T , typename Tarray > | |
| void | linspace (T x0, T x1, Tarray &target, int n) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | copyToArray (const adoreMatrix< T > &m, T *target) |
| template<typename T , long nr, long nc> | |
| void | copyToArray (const adoreMatrix< T, nr, nc > &m, T *target) |
| template<typename T , long nr, long nc> | |
| void | copyRowToArray (const adoreMatrix< T, nr, nc > &m, T *target, int col) |
| int | binomial (int n, int k) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | remainder (T x, T d) |
| template<typename T , long N> | |
| T | norm2 (const adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > &x) |
| template<typename T , long N> | |
| void | createAngularContinuity (adoreMatrix< T, N, 0 > &data, int row) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | comparePointWithLine (T a, T b, T c, T d, T e, T f, T &d_tangential, T &d_normal) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | getRelativeCoordinatesPointVSLine (T a, T b, T c, T d, T e, T f, T &d_tangential, T &d_normal) |
| template<typename T > | |
| double | getDistancePointToLine (T a, T b, T c, T d, T e, T f, T &rel, T &n) |
| template<typename T > | |
| double | getDistancePointToLine (T a, T b, T c, T d, T e, T f, T &rel) |
| template<typename T1 , typename T2 > | |
| bool | toRelativeWithNormalExtrapolation (double qX, double qY, const T1 pi, const T1 pj, const T2 ni, const T2 nj, double &s, double &t) |
| Transformation from Euclidean coordinate system to a relative coordinate system represented by linear-piecewise function xy and normal. The approximation of the originally non-linear function leads to inconsistencies with simpler methods. The following equation is fulfilled: q=pi+s/L*(pj-pi)+t*(ni+s/L*(nj-ni)) More... | |
| template<typename T1 , typename T2 > | |
| bool | toRelativeWithNormalExtrapolation (double qX, double qY, T1 centerline, T2 normals, double &s, double &t) |
| template<typename T1 , typename T2 > | |
| bool | fromRelative (double s, double t, const T1 pi, const T1 pj, const T2 ni, const T2 nj, double &X, double &Y, double &Z) |
| Transform from relative coordinates to Euclidean coordinates. More... | |
| template<typename T1 , typename T2 > | |
| void | fromRelative (double s, double t, T1 centerline, T2 normals, double &X, double &Y, double &Z) |
| transform from relative coordinates for given centerline and normal functions More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | intersectLines (T a, T b, T c, T d, T e, T f, T g, T h, T &x0, T &x1, bool &x0_inside, bool &x1_inside) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | intersectLines2 (T a, T b, T c, T d, T e, T f, T g, T h, T &x0, T &x1, T eps) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | bound (T lb, T value, T ub) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | bound (T lb, T value[], size_t count, T ub) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | annotatedDataOrdering_fct (std::pair< double, T > i, std::pair< double, T > j) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T * | cross (T *u, T *v, T *s) |
| template<int d, typename T > | |
| T | dot (T *u, T *v) |
| template<int k, typename T > | |
| T * | normalize (T *v) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | extendBounds (T &min, T value, T &max) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | overlaps (const T &a0, const T &a1, const T &b0, const T &b1) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | min (T a, T b, T c, T d) |
| template<typename T , long N, long M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, M > | min (adoreMatrix< T, N, M > a, const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > &b) |
| template<typename T , long N, long M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, M > | max (adoreMatrix< T, N, M > a, const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > &b) |
| double | min (double a, const double &b) |
| double | max (double a, const double &b) |
| float | min (float a, const float &b) |
| float | max (float a, const float &b) |
| int | min (int a, const int &b) |
| int | max (int a, const int &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| int | signum (T val) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| void | sample (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *f, T *x, T *y, int dimension, unsigned int count) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| void | sample (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *f, const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > &x, adoreMatrix< T, N, 0 > &y, unsigned int K, int offset=0) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| void | sample (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *f, T *x, T *y, unsigned int count) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| void | sample (AScalarToN< T, N > *f, const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > &x, adoreMatrix< T, N, 0 > &y, unsigned int K, int offset=0) |
| int | computeLaneWidthAndCenter (const adoreMatrix< double, 0, 0 > &left, const adoreMatrix< double, 0, 0 > &right, adoreMatrix< double, 0, 0 > ¢er) |
| int | computeLaneWidthAndCenter (const LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 3 > &left, const LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 3 > &right, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 4 > ¢er) |
| int | computeCenterline (const adoreMatrix< double, 0, 0 > &left, const adoreMatrix< double, 0, 0 > &right, adoreMatrix< double, 0, 0 > ¢er) |
| int | computeCenterline (const LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 3 > &left, const LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 3 > &right, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< double, 3 > ¢er) |
| template<typename T > | |
| ALFunction< T, T > * | sample_curvature (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, 2, 1 >> *path, adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > samples) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const interval< T > &obj) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator< (const interval< T > &lhs, const interval< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator> (const interval< T > &lhs, const interval< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator<= (const interval< T > &lhs, const interval< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator>= (const interval< T > &lhs, const interval< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator!= (const interval< T > &lhs, const interval< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator== (const interval< T > &lhs, const interval< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| adoreMatrix< interval< T >, N, M > | create_interval (const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > &lb, const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > &ub) |
| template<typename T > | |
| interval< T > | create_interval (const T &lb, const T &ub) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, M > | lower_bound (const adoreMatrix< interval< T >, N, M > &data) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | lower_bound (const interval< T > &iv) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, M > | upper_bound (const adoreMatrix< interval< T >, N, M > &data) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | upper_bound (const interval< T > &iv) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M, int K> | |
| void | imultiply (const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > &lba, const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > &uba, const adoreMatrix< T, M, K > &lbb, const adoreMatrix< T, M, K > &ubb, adoreMatrix< T, N, K > &lb, adoreMatrix< T, N, K > &ub) |
| template<typename T , long N> | |
| void | imultiply (const adoreMatrix< T, N, 1l > &lba, const adoreMatrix< T, N, 1l > &uba, const double &lbb, const double &ubb, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1l > &lb, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1l > &ub) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M, int K> | |
| void | imultiply (const adoreMatrix< interval< T >, N, M > &a, const adoreMatrix< interval< T >, M, K > &b, adoreMatrix< T, N, K > &lb, adoreMatrix< T, N, K > &ub) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | imultiply (const interval< T > &a, const interval< T > &b, T &lb, T &ub) |
| void | imultiply (const double &lba, const double &uba, const double &lbb, const double &ubb, double &lb, double &ub) |
| template<typename T > | |
| interval< T > | sin (interval< T > x) |
| template<typename T > | |
| interval< T > | cos (interval< T > x) |
| template<typename T > | |
| interval< T > | atan2 (interval< T > y, interval< T > x) |
| template<typename T , int dout, int din> | |
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dout > | getSubFunction (LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, din > &fin, int dimensions[dout]) |
| template<typename T , int n_dfun, int n_base, int n_normal, int n_target> | |
| void | defineDistanceMap2d (LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_dfun > *dfun, int id, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_base > *base, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_normal > *normal, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_target > *target, T guard, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, 1 > *guardfun=0) |
| template<typename T > | |
| LPiecewiseFunction< T, T > * | createPiecewiseLinear (const adoreMatrix< T, 2, 0 > &xymatrix) |
| template<typename T > | |
| LPiecewiseFunction< T, T > * | createPiecewiseLinear (const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > &xvec, const adoreMatrix< T > &yvec, int row) |
| template<typename T , int n> | |
| LPiecewiseFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, n, 1 > > * | createPiecewiseLinear (const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > &xvec, const adoreMatrix< T, n, 0 > &ymatrix) |
| template<typename T , int n> | |
| LPiecewiseFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, n, 1 > > * | createPiecewiseLinear (const adoreMatrix< T, n+1, 0 > &xymatrix) |
| template<typename T , int n> | |
| void | sample (LPiecewiseFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, n, 1 >> *fun, T *xvec, T *ydest, int row, int count) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| void | poly_parameter_derivative (adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > &p) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > | evaluate_poly (const adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > &data, const T &x) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > | stretch_poly_parameters (adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > data, const T &a, const T &b, const T &c, const T &d) |
| template<typename T , int M> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, 1, M+1 > | poly_parameter_for_initial_condition (adoreMatrix< T, M+1, 1 > c) |
| template<typename T , int N, int M> | |
| void | bound_poly (const adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > &data, const T &x0, const T &x1, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > &ymin, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > &ymax) |
| template<typename T , int d> | |
| void | define_integrator_chain (dlib::matrix< T, d, d > &Ad, dlib::matrix< T, d, 1 > &Bd, T dt) |
| template<typename T > | |
| ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, 2, 1 > > * | create_normalOffset (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, 2, 1 >> *path, ALFunction< T, T > *heading, ALFunction< T, T > *distance) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, N, N > | rotationMatrix (T angle) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > & | path_distance (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *path, const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > &x) |
| template<typename T , int N> | |
| ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, 2, 1 > > * | create_trueDistancePath (ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> *path, int count) |
| template<typename T , int dtun_center, int dtun_left, int dtun_right, int dfin> | |
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, 4 > | getTunnelProjection (LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dtun_center > *tunnel_center, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dtun_left > *tunnel_left, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dtun_right > *tunnel_right, LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dfin > *finput, T winput, int ixtun=1, int iytun=2, int idleft=1, int idright=1, int ixin=1, int iyin=2) |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<double, 2> adore::mad::function_type2d |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<double, 1> adore::mad::function_type_scalar |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<double, 3> adore::mad::function_type_xyz |
| typedef interval<double> adore::mad::idouble |
| typedef interval<float> adore::mad::ifloat |
| typedef interval<int> adore::mad::iint |
| typedef adore::mad::LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<double, 1> adore::mad::velocity_profile |
| bool adore::mad::annotatedDataOrdering_fct | ( | std::pair< double, T > | i, |
| std::pair< double, T > | j | ||
| ) |
annotatedDataOrdering_fct - helps to sort double-annotated data of type std::pair(double,T) with std::sort
interval atan2
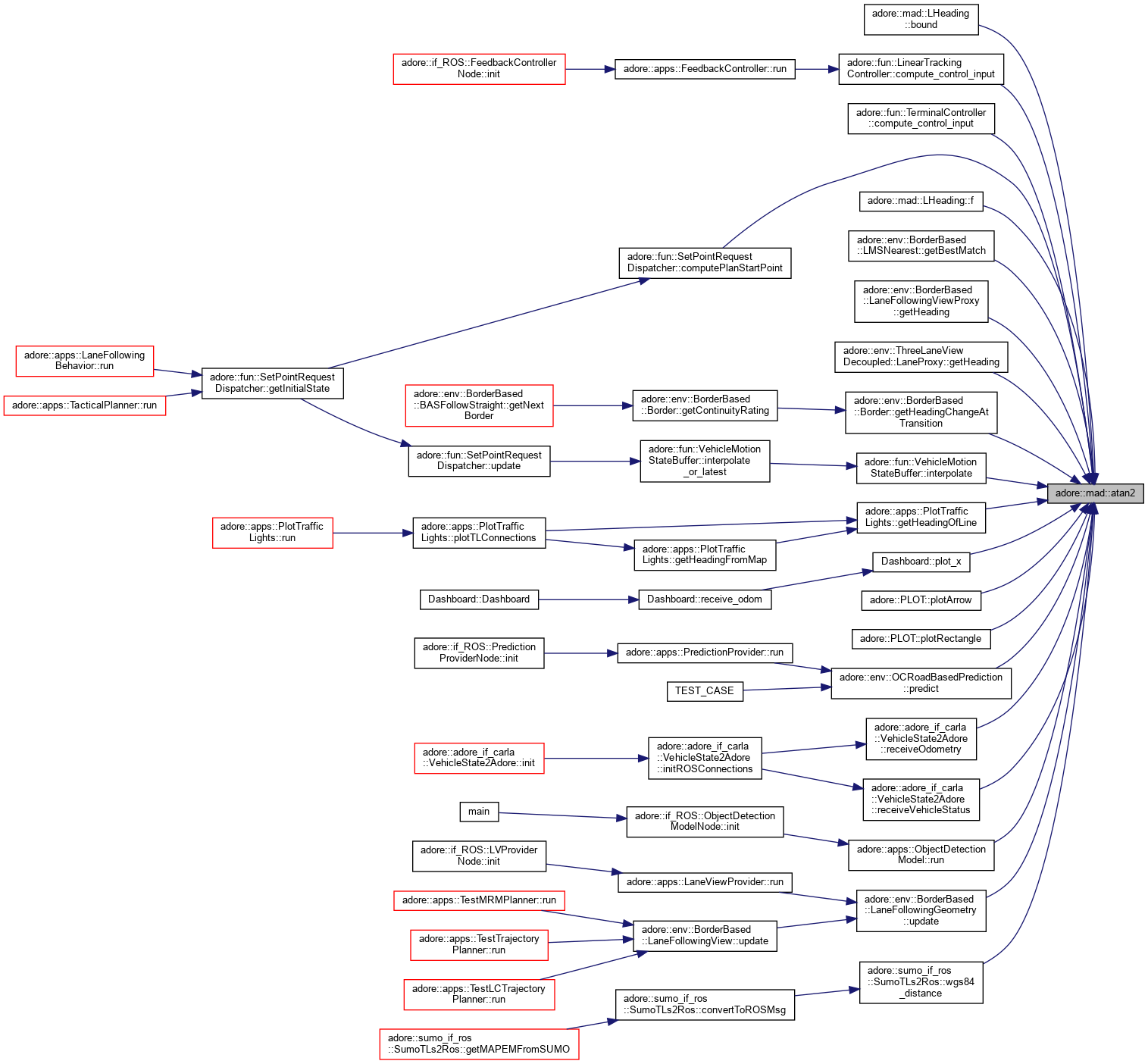
|
inline |
n �ber k, n choose k, as given in https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15301885/calculate-value-of-n-choose-k
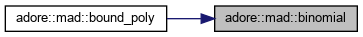
|
inline |
bound - bounding a value above and below
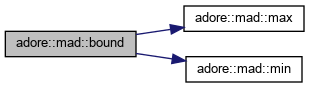
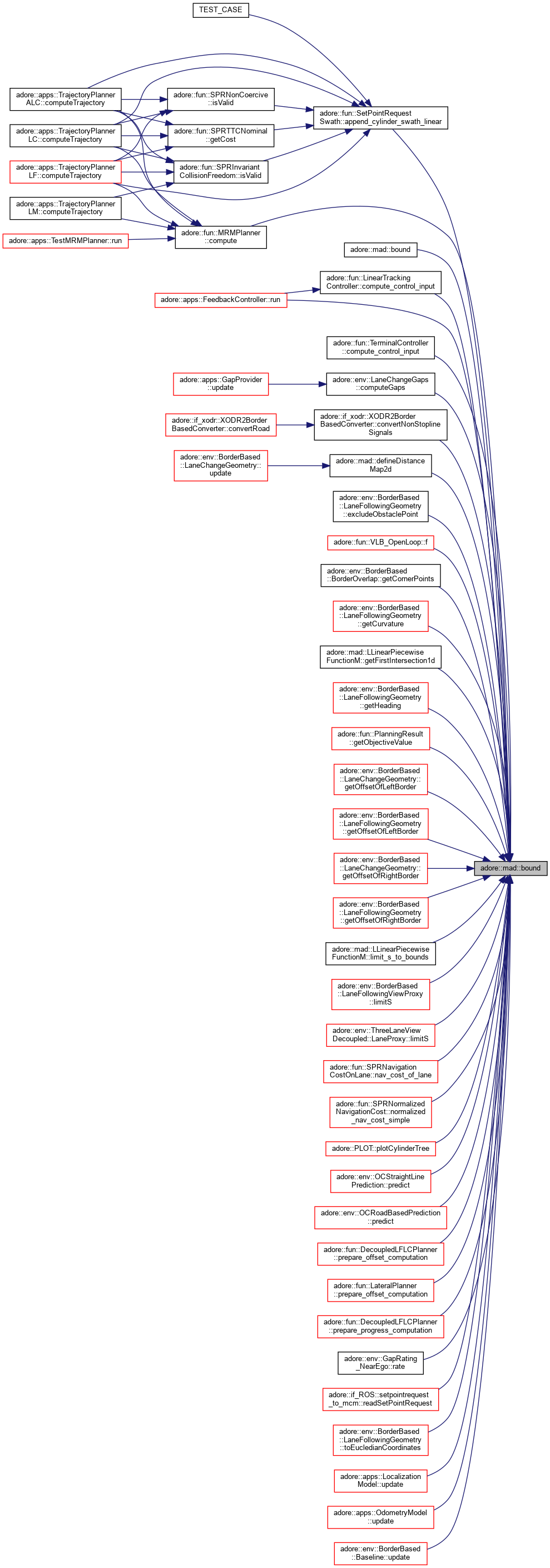
|
inline |
bound - bounding a value above and below

| void adore::mad::bound_poly | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > & | data, |
| const T & | x0, | ||
| const T & | x1, | ||
| adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > & | ymin, | ||
| adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > & | ymax | ||
| ) |
compute bounds on polynomial according to Cargo, Shisha 1965: The Bernstein Form of a Polynomial first the polynomial is normalized to the interval x\in[0,1], then the bernstein form is used to bound y'([0,1])
|
inline |
computes the position of a point relative to a line line (a,b)->(c,d), point (e,f) d_tangential is in [0,1] if point is projected inside line, is >1 if point is in front and <0 if point is behind d_normal is >0 if point is left of line and <0 if right of line. d_normal is also the normal distance
|
inline |
computes the centerline between two point-lists of size N and M. the resulting point list has size N+M-1. N>=2 and M>=2 required. left is of size dxN, right is of size dxM, center is of size dx(N+M-2), with d>=4, so that a matrix is ( (s0,x0,y0,z0,...)^T (s1,x1,y1,z1,...)^T ... ) the center matrix must be sufficiently sized before computeCenterline. Redundant points are removed from centerline, so that the actual number of distinct points is returned.

|
inline |
|
inline |
computes the distance and the center between two point-lists of size N and M. the resulting point list has size N+M-1. N>=2 and M>=2 required. left is of size dxN, right is of size dxM, center is of size (d+1)x(N+M-2), with d>=4, so that a matrix is ( (s0,x0,y0,z0,w0,...)^T (s1,x1,y1,z1,w1...)^T ... ) where w0, w1, ... is the width of the lane. the center matrix must be sufficiently sized before computeLaneWidthAndCenter. Redundant points are removed from center, so that the actual number of distinct points is returned.

|
inline |
| void adore::mad::copyRowToArray | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, nr, nc > & | m, |
| T * | target, | ||
| int | col | ||
| ) |
copy a single row from a matrix to an array
| void adore::mad::copyToArray | ( | const adoreMatrix< T > & | m, |
| T * | target | ||
| ) |
copy values from a matrix into an array
| void adore::mad::copyToArray | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, nr, nc > & | m, |
| T * | target | ||
| ) |
copy values from a matrix into an array
interval cos
| adoreMatrix<interval<T>, N, M> adore::mad::create_interval | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > & | lb, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > & | ub | ||
| ) |
| interval<T> adore::mad::create_interval | ( | const T & | lb, |
| const T & | ub | ||
| ) |
| ALFunction<T, adoreMatrix<T, 2, 1> >* adore::mad::create_normalOffset | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, 2, 1 >> * | path, |
| ALFunction< T, T > * | heading, | ||
| ALFunction< T, T > * | distance | ||
| ) |
Create a 2d-path, which is normally offset at a given distance from another path.
| path | the reference path |
| heading | the heading of the reference path |
| distance | the offset |
| ALFunction<T, adoreMatrix<T, 2, 1> >* adore::mad::create_trueDistancePath | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | path, |
| int | count | ||
| ) |
create_trueDistancePath - creates a function object, which indexes the given path via true distance instead of its previous parameter. The function is created by computing the distance and chaining the inverse distance function with a clone of the path: d:x->s, => f: p(d^-1(s)) N is the dimension of the path - usually 2 for 2D paths, but could be 3D count is the number of samples to take for the distance function
| path | Two dimensional path to be evaluated |
| count | number of samples |
| void adore::mad::createAngularContinuity | ( | adoreMatrix< T, N, 0 > & | data, |
| int | row | ||
| ) |
createAngularContinuity - correct jumps from +pi+\epsilon to -pi+\epsilon If a linear piecewise representation of angles is interpolated, these jumps can lead to almost any result on the circle. To correct, angles are counted further than pi. Corrections are applied to data(row,:)
| LPiecewiseFunction<T, T>* adore::mad::createPiecewiseLinear | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > & | xvec, |
| const adoreMatrix< T > & | yvec, | ||
| int | row | ||
| ) |
| LPiecewiseFunction<T, adoreMatrix<T, n, 1> >* adore::mad::createPiecewiseLinear | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > & | xvec, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, n, 0 > & | ymatrix | ||
| ) |
| LPiecewiseFunction<T, T>* adore::mad::createPiecewiseLinear | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, 2, 0 > & | xymatrix | ) |
| LPiecewiseFunction<T, adoreMatrix<T, n, 1> >* adore::mad::createPiecewiseLinear | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, n+1, 0 > & | xymatrix | ) |
| T* adore::mad::cross | ( | T * | u, |
| T * | v, | ||
| T * | s | ||
| ) |
cross product for c-arrays: s:=u x v
| void adore::mad::define_integrator_chain | ( | dlib::matrix< T, d, d > & | Ad, |
| dlib::matrix< T, d, 1 > & | Bd, | ||
| T | dt | ||
| ) |
define discrete time system matrix for an integrator chain
| Ad | discrete time system matrix, result |
| Bd | discrete time input matrix, result |
| T | time step |
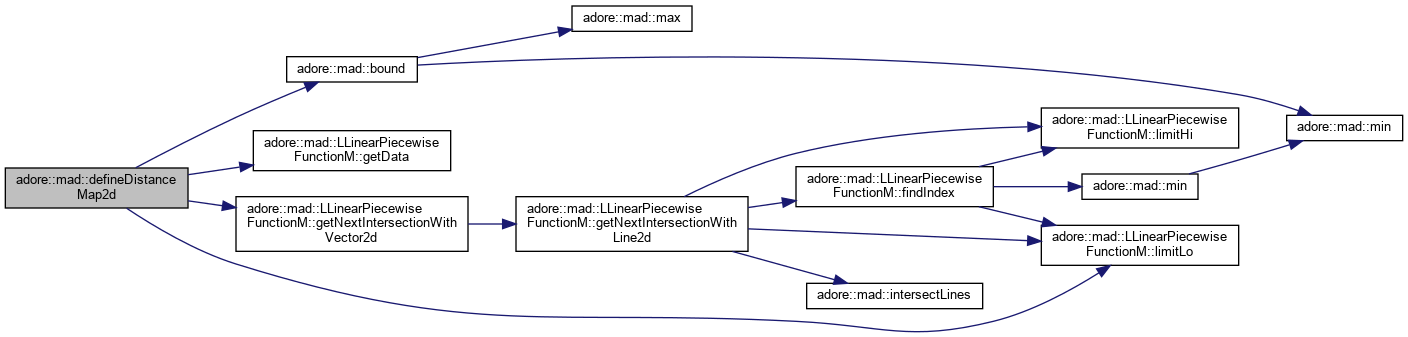
| void adore::mad::defineDistanceMap2d | ( | LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_dfun > * | dfun, |
| int | id, | ||
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_base > * | base, | ||
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_normal > * | normal, | ||
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, n_target > * | target, | ||
| T | guard, | ||
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, 1 > * | guardfun = 0 |
||
| ) |
defineDistanceMap - defines dfun's i-th row to be d(t), with target(s)=base(t)+normal(t)*d(t)*scale. d is computed for each sampling point of base. If dfun.nc() is smaller than base nc(), this data is resized and therefore all previous values are lost. this sampling is set to equal the sampling of base. If target or n have smaller domains than base, values outside their domain are assigned with either guard or guardfun. if guardfun==0, guard constant guard value is used outside domain otherwise, guardfun is sampled

| T adore::mad::dot | ( | T * | u, |
| T * | v | ||
| ) |
dot product for c-arrays: val:=u'*v
| adoreMatrix<T, N, 1> adore::mad::evaluate_poly | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > & | data, |
| const T & | x | ||
| ) |
evaluate a polynomial \mathbb{R}->\mathbb{R}^N: y=p0 + p1 x +p2 x� + pM x^M, given a parameter matrix data=[p0,p1,p2...] and a value x
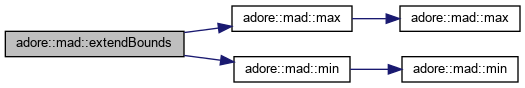
| void adore::mad::extendBounds | ( | T & | min, |
| T | value, | ||
| T & | max | ||
| ) |
extend min and max to contain value
| bool adore::mad::fromRelative | ( | double | s, |
| double | t, | ||
| const T1 | pi, | ||
| const T1 | pj, | ||
| const T2 | ni, | ||
| const T2 | nj, | ||
| double & | X, | ||
| double & | Y, | ||
| double & | Z | ||
| ) |
Transform from relative coordinates to Euclidean coordinates.
| s | relative coordinate transversal component |
| t | relative coordinate lateral component |
| pi | first point of baseline (si,xi,yi) |
| pj | last point of baseline (si,xi,yi) |
| ni | first normal of baseline (nxi,nyi) |
| nj | last normal of baseline (nxj,nyj) |
| X | output, Euclidean x component |
| Y | output, Euclidean y component |
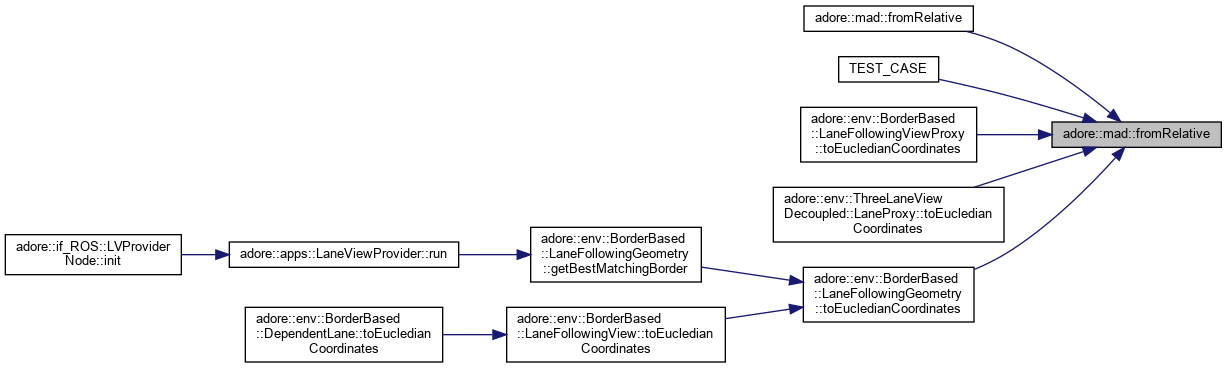
| void adore::mad::fromRelative | ( | double | s, |
| double | t, | ||
| T1 | centerline, | ||
| T2 | normals, | ||
| double & | X, | ||
| double & | Y, | ||
| double & | Z | ||
| ) |
transform from relative coordinates for given centerline and normal functions
| s | relative coordinate transversal component |
| t | relative coordinate lateral component |
| centerline | centerline function s->(X,Y,..) of type LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM* |
| normals | normal function s->(nx,ny) of type LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM* |

|
inline |
|
inline |
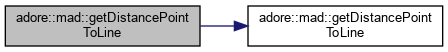
computes the distance between a line and a point and saves the relative progress in rel line (a,b)->(c,d), point (e,f)
|
inline |
computes the longitudinal and lateral position wrt a line line (a,b)->(c,d), point (e,f)
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<T,dout> adore::mad::getSubFunction | ( | LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, din > & | fin, |
| int | dimensions[dout] | ||
| ) |
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<T,4> adore::mad::getTunnelProjection | ( | LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dtun_center > * | tunnel_center, |
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dtun_left > * | tunnel_left, | ||
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dtun_right > * | tunnel_right, | ||
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM< T, dfin > * | finput, | ||
| T | winput, | ||
| int | ixtun = 1, |
||
| int | iytun = 2, |
||
| int | idleft = 1, |
||
| int | idright = 1, |
||
| int | ixin = 1, |
||
| int | iyin = 2 |
||
| ) |
Computes a peculiar projection, "tunnel projection", which is useful for matching positions on lanes
| tunnel_center | a function s |-> x_tun,y_tun, mapping centerline from distance along centerline to Cartesian |
| tunnel_left | a function s |-> d_left, distance from center to left tunnel wall |
| tunnel_right | a funciton s |-> d_right, distance from center to right tunnel wall |
| finput | a function t |-> (x_in,y_in), input function, which has to be projected, mapping from a parameter t to Cartesian: finput represents center of swath |
| winput | width of the input swath |
|
inline |
interval multiplication for NxM * MxK
|
inline |
interval multiplication for Nx1 * double
|
inline |
interval multiplication for NxM * MxK
|
inline |
interval multiplication for double * double
|
inline |
interval multiplication for double * double
|
inline |
(a,b)->(c,d); (e,f)->(g,h) returns true, if the lines are not parallel sets x0 and x1 to the parameter of the intersection point, ip = (a,b)+x0*(c,d-a,b) sets x0_inside to true, if the intersection point is between (a,b) and (c,d) sets x1_inside to true, if the intersection point is between (e,f) and (g,h)
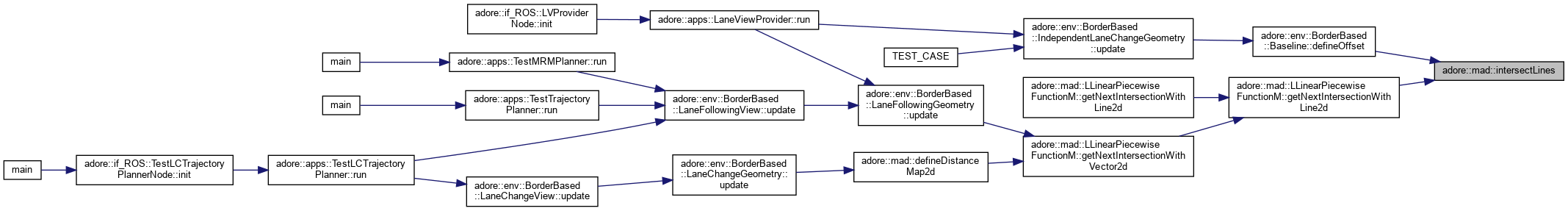
|
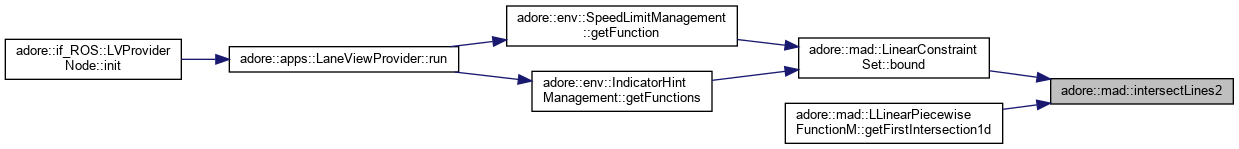
inline |
(a,b)->(c,d); (e,f)->(g,h) returns true, if the lines intersect: true crossing>eps, not only touching sets x0 and x1 to the parameter of the intersection point, ip = (a,b)+x0*(c,d-a,b) sets x0_inside to true, if the intersection point is between (a,b) and (c,d) sets x1_inside to true, if the intersection point is between (e,f) and (g,h)
| adoreMatrix<T, 1, n> adore::mad::linspace | ( | T | x0, |
| T | x1 | ||
| ) |
provides a statically sized vector with n values evenly spaced between x0 and x1
resolve rounding problem to not exceed limit
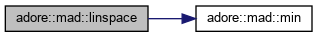
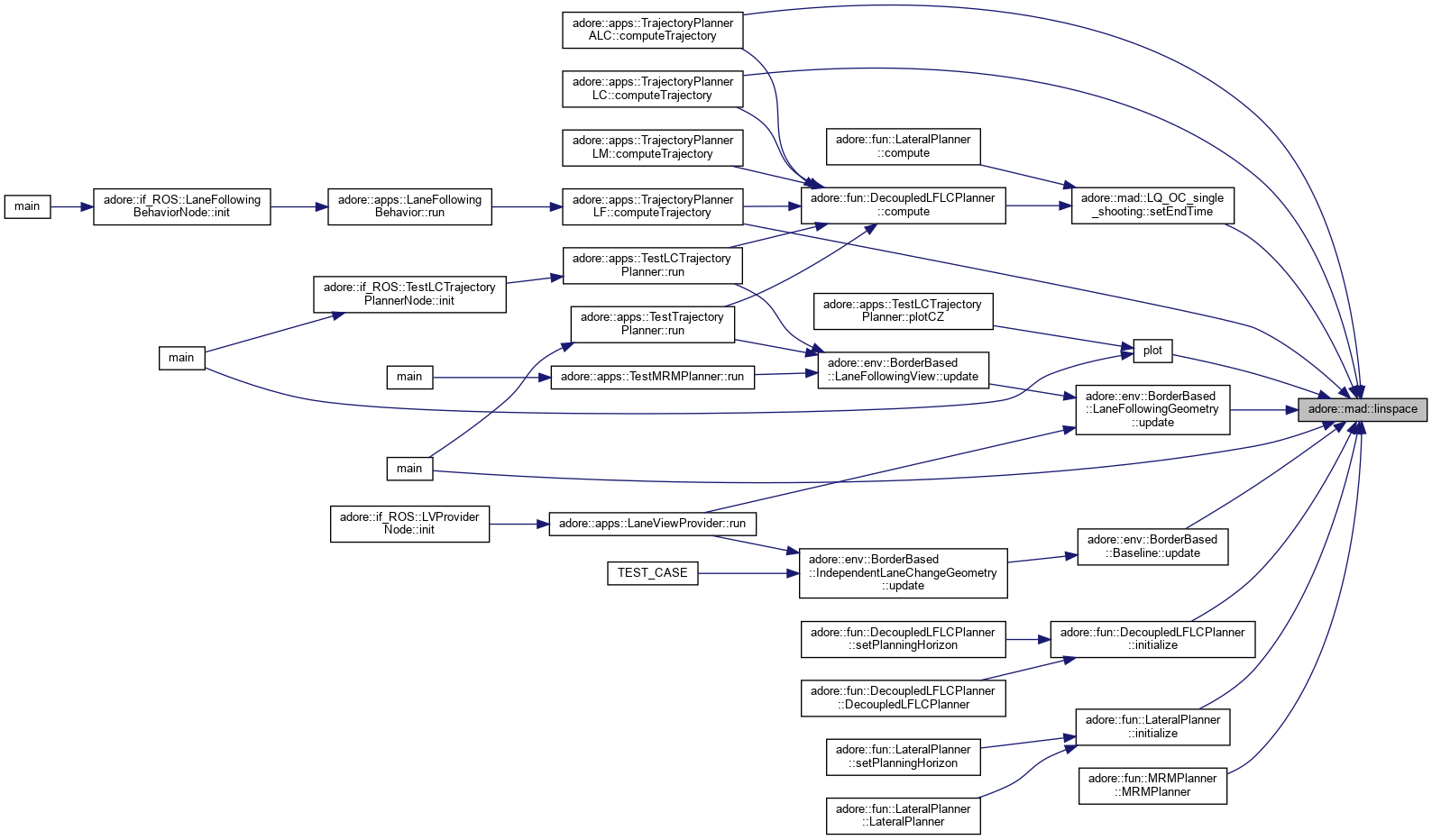
| adoreMatrix<T, 1, 0> adore::mad::linspace | ( | T | x0, |
| T | x1, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) |
provides a dynamically sized vector with n values evenly spaced between x0 and x1
resolve rounding problem to not exceed limit
| void adore::mad::linspace | ( | T | x0, |
| T | x1, | ||
| Tarray & | target, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) |
fills an array with n values evenly spaced between x0 and x1
resolve rounding problem to not exceed limit
| adoreMatrix<T, N, M> adore::mad::lower_bound | ( | const adoreMatrix< interval< T >, N, M > & | data | ) |
| T adore::mad::lower_bound | ( | const interval< T > & | iv | ) |
| adoreMatrix<T, N, M> adore::mad::max | ( | adoreMatrix< T, N, M > | a, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > & | b | ||
| ) |
max applied to two vectors

|
inline |

|
inline |

|
inline |
| adoreMatrix<T, N, M> adore::mad::min | ( | adoreMatrix< T, N, M > | a, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, N, M > & | b | ||
| ) |
min applied to two vectors

|
inline |

|
inline |

|
inline |
| T adore::mad::min | ( | T | a, |
| T | b, | ||
| T | c, | ||
| T | d | ||
| ) |
the minimum of four values

| T adore::mad::norm2 | ( | const adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 > & | x | ) |
computes the 2 norm of a vector x

| T* adore::mad::normalize | ( | T * | v | ) |
normalize length of a vector
|
inline |
|
inline |
| std::ostream& adore::mad::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| const interval< T > & | obj | ||
| ) |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
| bool adore::mad::overlaps | ( | const T & | a0, |
| const T & | a1, | ||
| const T & | b0, | ||
| const T & | b1 | ||
| ) |
test whether two intervals overlap
| adoreMatrix<T, 1, 0>& adore::mad::path_distance | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | path, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > & | x | ||
| ) |
path_distance - computes the distance along a path by sampling the path derivative at fixed steps defined in x a matrix d is returned, which contains the cummulatitve sum (is therefore sorted) N is the dimension of the path - usually 2 for 2D paths, but could be 3D
| path | Two dimensional path to be evaluated |
| x | Samples of path's domain |
| void adore::mad::poly_parameter_derivative | ( | adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > & | p | ) |
given a set of parameters p of a polynomial y=p0 + p1 x +p2 x� +..., compute the parameters of the derivative y'=p1 + 2p2 x+ 3p3 + ...,
| adoreMatrix<T, 1, M + 1> adore::mad::poly_parameter_for_initial_condition | ( | adoreMatrix< T, M+1, 1 > | c | ) |
create polynomial parameters y=p0 + p1 x +p2 x� +... for a polynomial of degree M which satisfy an initial condition vector c, with y^(i)(0)=c(i), with c sized (M+1)x1 (allowing to create a polynomial for an integrator chain)
| T adore::mad::remainder | ( | T | x, |
| T | d | ||
| ) |
computes the remainder of x/d
| adoreMatrix<T, N, N> adore::mad::rotationMatrix | ( | T | angle | ) |
| void adore::mad::sample | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | f, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > & | x, | ||
| adoreMatrix< T, N, 0 > & | y, | ||
| unsigned int | K, | ||
| int | offset = 0 |
||
| ) |
compute function value at multiple points x of the domain
| f | the function to be evaluated |
| x | array of samples of the domain |
| y | matrix for query results |
| K | number of samples |
| offset | dimension shift in target array y |
| void adore::mad::sample | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | f, |
| T * | x, | ||
| T * | y, | ||
| int | dimension, | ||
| unsigned int | count | ||
| ) |
compute function value in a given codomain dimension at multiple points x of the domain
| f | the function to be evaluated |
| x | array of samples of the domain |
| y | array for query results |
| dimension | index of codomain-dimension |
| count | number of samples |
| void adore::mad::sample | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | f, |
| T * | x, | ||
| T * | y, | ||
| unsigned int | count | ||
| ) |
compute function value at multiple points x of the domain
| f | the function to be evaluated |
| x | array of samples of the domain |
| y | array for query results |
| count | number of samples |
| void adore::mad::sample | ( | AScalarToN< T, N > * | f, |
| const adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > & | x, | ||
| adoreMatrix< T, N, 0 > & | y, | ||
| unsigned int | K, | ||
| int | offset = 0 |
||
| ) |
compute function value at multiple points x of the domain
| f | the function to be evaluated |
| x | array of samples of the domain |
| y | matrix for query results |
| K | number of samples |
| offset | dimension shift in target array y |
| void adore::mad::sample | ( | LPiecewiseFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, n, 1 >> * | fun, |
| T * | xvec, | ||
| T * | ydest, | ||
| int | row, | ||
| int | count | ||
| ) |
| LLinearPiecewiseFunctionM<T, N>* adore::mad::sample_adaptive | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | f, |
| ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, N, 1 >> * | df, | ||
| T | edes, | ||
| T | emax, | ||
| T | xmin, | ||
| T | xmax, | ||
| T | xstep, | ||
| T | precision = (T)0.0001 |
||
| ) |
sample_adaptive - error sensitive sampling of points of a function provide function f, derivative df and a maximum error emax the sampling error is defined as normal distance between the returned pw linear approximation and f
| T | is the numeric type, e.g. float or double |
| N | is the number of the functions' codomain dimensions |
| f | f is the function to be sampled |
| df | df is the derivative of f |
| edes | edes is the desired sampling error (tradeoff between number of points and precision) |
| emax | is an upper bound on the maximum error, which has to be guaranteed by the sampling strategy |
| xmin | is a lower bound on the stepsize |
| xmax | is an upper bound on the stepsize |
| xstep | is the current/starting stepsize, xstep must be greater than 0 |
| ALFunction<T, T>* adore::mad::sample_curvature | ( | ALFunction< T, adoreMatrix< T, 2, 1 >> * | path, |
| adoreMatrix< T, 1, 0 > | samples | ||
| ) |
compute curvature of a path
| path | function mapping from path parameter to X and Y, the path for which curvature is computed |
| samples | vector of path parameters at which curvature is evaluated |
| void adore::mad::sequence | ( | T | x0, |
| T | dx, | ||
| T * | target, | ||
| int | size | ||
| ) |
fills an array with a sequence of values
| adoreMatrix<T, 1, 0> adore::mad::sequence | ( | T | x0, |
| T | dx, | ||
| T | xend | ||
| ) |
provides a vector filled with a sequence of values
| int adore::mad::sequence | ( | T | x0, |
| T | dx, | ||
| T | xend, | ||
| T * | target, | ||
| int | max_size | ||
| ) |
fills an array with a sequence of values
| void adore::mad::set | ( | T * | data, |
| T | value, | ||
| int | size | ||
| ) |
initialize an array with data
|
inline |

interval sin

| adoreMatrix<T, N, M + 1> adore::mad::stretch_poly_parameters | ( | adoreMatrix< T, N, M+1 > | data, |
| const T & | a, | ||
| const T & | b, | ||
| const T & | c, | ||
| const T & | d | ||
| ) |
given a set of parameters p of a polynomial y=p0 + p1 x +p2 x� +..., create a set of parameters q for a polynomial y_s, so that y_s([c,d])=y([a,b]), e.g. compute parameters for y_s(x)=y((x-c)/(d-c)*(b-a)+a) task is also known as "polynomial shift"
| bool adore::mad::toRelativeWithNormalExtrapolation | ( | double | qX, |
| double | qY, | ||
| const T1 | pi, | ||
| const T1 | pj, | ||
| const T2 | ni, | ||
| const T2 | nj, | ||
| double & | s, | ||
| double & | t | ||
| ) |
Transformation from Euclidean coordinate system to a relative coordinate system represented by linear-piecewise function xy and normal. The approximation of the originally non-linear function leads to inconsistencies with simpler methods. The following equation is fulfilled: q=pi+s/L*(pj-pi)+t*(ni+s/L*(nj-ni))
| qX | the point to be transformed, X component |
| qY | the point to be transformed, Y component |
| pi | the initial point of the linearly approximated baseline (pis,pix,piy) |
| pj | the final point of the linearly approximated baseline (pjs,pjx,pjy) |
| ni | the initial normal vector (nix,niy) |
| nj | the final normal vector (njx,njy) |
| s | output: relative coordinate transversal component |
| t | output: relative coordinate lateral component |
| bool adore::mad::toRelativeWithNormalExtrapolation | ( | double | qX, |
| double | qY, | ||
| T1 | centerline, | ||
| T2 | normals, | ||
| double & | s, | ||
| double & | t | ||
| ) |
| adoreMatrix<T, N, M> adore::mad::upper_bound | ( | const adoreMatrix< interval< T >, N, M > & | data | ) |
| T adore::mad::upper_bound | ( | const interval< T > & | iv | ) |